What are the typical features to look for in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in each of the following investigations?
Click on the links below.
ECG
ECG
- Left atrial enlargement
- Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH)
- Pathological Q waves (typically inferolaterally)
- Giant negative T waves
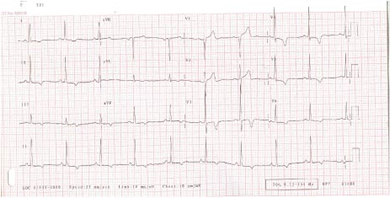
Fig 1 ECG of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy showing LVH and T wave changes
What are the typical features to look for in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in each of the following investigations?
Click on the links below.
Echocardiogram
Echocardiogram
Typical features include:
- Left ventricular hypertrophy – any pattern possible, but typically asymmetrical septal hypertrophy
- Small LV cavity size
- Increased ejection fraction
- Left atrial enlargement
- Resting left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) due to contact between anterior mitral valve leaflet and septum in systole (occurs in 25% of patients)
- Systolic anterior motion (SAM) of mitral valve leaflet
- LVOTO can be absent on rest scanning but be provokable with Valsalva manoeuvre or exercise
- Premature closure of aortic valve
- Mitral regurgitation
What are the typical features to look for in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in each of the following investigations?
Click on the links below.
- Video 1
- Video 2
What are the typical features to look for in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in each of the following investigations?
Click on the links below.
- Video 1
- Video 2
What are the typical features to look for in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in each of the following investigations?
Click on the links below.
Exercise test
Exercise test
The patient should complete an exercise test using a standard treadmill or bicycle protocol. It can be an exercise test or a cardiopulmonary exercise stress test. The important information that requires recording is listed below:
- Exercise duration and workload completed
- Blood pressure response to exercise (a fall in blood pressure during the test or a failure to rise ≥25 mmHg from baseline during the test is considered significant)
- Whether there are atrial or ventricular arrhythmias recorded
What are the typical features to look for in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in each of the following investigations?
Click on the links below.
Holter monitoring
Holter monitoring
Assess for atrial and ventricular arrhythmias.
It is especially important to assess for ventricular arrhythmias, as even three beats of ventricular tachycardia can represent an increased risk of sudden cardiac death.
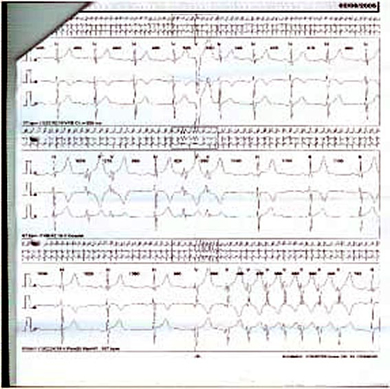
Fig 4 Holter monitor showing non-sustained ventricular tachycardia in the bottom panel
What are the typical features to look for in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in each of the following investigations?
Click on the links below.
MRI scan
MRI scan
MRI scans constitute an important part, they:
- May be helpful in selected cases where echo imaging is difficult
- Are also useful to assess right ventricular or left ventricular apical involvement
- Can determine the extent of myocardial fibrosis
What are the typical features to look for in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in each of the following investigations?
Click on the links below.
Cardiac catheterisation
Cardiac catheterisation
This is very important for different reasons:
- Used to exclude coronary atherosclerosis as a cause of exertional chest pain and show cavity obliteration on ventriculogram
- Right heart catheterisation can assess for restrictive physiology
- Can be used to confirm the presence of left ventricular outflow obstruction and severity of mitral regurgitation
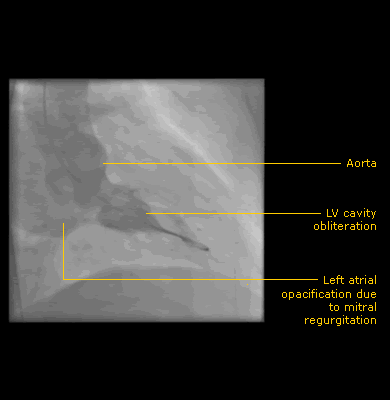
Fig 5 Left ventriculogram showing systolic cavity obliteration